A ketogenic diet requires you to eat less carbs, more fat and protein. As you follow this diet, you will see that excessive fat deposits are being burned by the body. It may be challenging at first, but a keto diet is known for weight loss in a fast way. It also does not have any detrimental effects on your health. On the contrary, research has even noted that a high –fat diet in keto can decrease body weight and improve health.
However, as research continues on the topic of ketogenic diet, there is a growing perception among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus that it has negative effects on their health. It is perceived that insulin levels are not used by the body when blood glucose levels decrease. Research includes risk factors of developing type 2 diabetes among people who are already genetically at risk. In this article, we aim to present you with clear arguments from both sides of the effects of ketogenic diet for insulin resistance. We hope by the end you are able to decide whether to follow this diet or not.
What Is Insulin Resistance and Why It Matters
In this article, we start with the basics. Let’s look into what insulin is and how the body works to metabolise insulin to manage sugar levels. Low carbohydrate diet induces low blood sugar and other diets can also improve insulin, but to understand this, here are the basics:
Role of Insulin in Metabolism
Insulin is a hormone that is produced in our body by the pancreas. As it is released into the blood stream, insulin maintains a glucose homeostasis in the body. This means that it attains optimal levels of sugar in the blood.
The way that it does it is by encouraging various metabolisms within the body, which help in uptake of excessive sugar. For example, glucose acts as a regulator for lipid metabolism, a process which requires glucose and creates lipid proteins. Levels of glucose and insulin form a sort of equilibrium in the body, ensuring other processes go by optimally.
Insulin Resistance and Its Link to Diabetes
Insulin also regulates glucose uptake by the cells in your body. If an insulin molecule is present near a cell, then it stops a glucose molecule from absorption. If glucose levels are too high, this helps to regulate blood glucose.
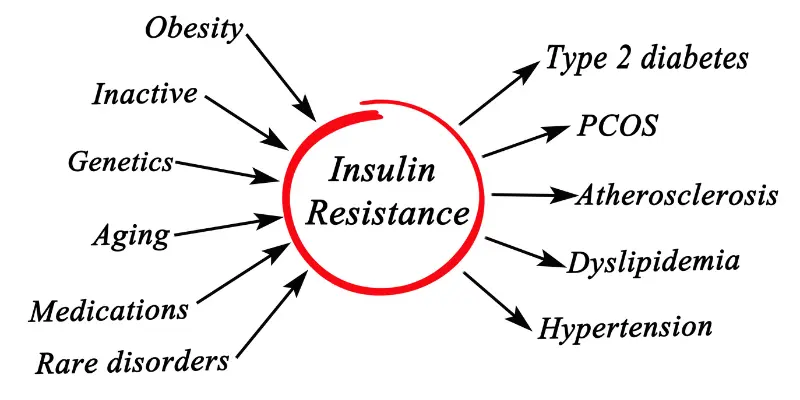
However, patients with type 2 diabetes or other immune diseases related to insulin resistance, it has been noticed that insulin is unable to regulate glucose because cells do no respond to glucose. Whether the cells make us fatty deposits, muscles, liver or even the heart, they simply do not respond to insulin signals and keep taking up glucose. This is called as insulin resistance.
In normal bodily functions, if insulin resistance occurs, then your pancreas simply creates more insulin. However, when resistance persists, then the person is diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. It can be limited to a region of cells, like hepatic insulin resistance, when liver becomes insulin resistant. These mechanisms of insulin resistance form the basic Aetiology of type 2 diabetes.
Statistics on Rising Rates of Insulin Resistance Globally
- Currently, there are 463 million people with type 2 diabetes, i.e. they have insulin resistance
- This number will rise to 700 million in 2045
- Only in the UK, 40% of adults have been diagnosed with insulin resistance
- People of all ages are insulin resistance, from 18 year olds to even 44 year olds
- Most cases (89%) occur in middle income and low income countries.
What is a Keto Diet and How It May Impact Insulin Sensitivity?
The next step is now to review a ketogenic diet. Most of us have heard of keto, but there is a whole science behind it that we discover now
Definition of Ketogenic Diet: Very Low Carb, High Fat
If your diet is low on carbs and high in fat, then it is a keto diet. With this diet, your body reaches a state of ketosis. It is when excessive fat deposits are being burnt for energy in the body, which would normally be taken from carbs. Effects of ketogenic diet is that the diet may cause weight loss within a short span of time
Potential Mechanisms:
- Lowering Blood Glucose
Reaching a state of ketosis varies from person to person. It can take days or even weeks, but no longer than that. You are not receiving glucose from carbohydrates because your carbohydrate ketogenic diet is low. Your body then shifts to using ketones to create energy. Ketones are made from burning fat, so glucose remains low and fat is also burned
- Reducing Inflammation
When you follow a normal diet, it is very different to what happens in your body with keto. So in the initial days when you switch to a low carbohydrate diet, your body responds to the change. It does so by protecting the organs, which naturally reduces inflammation.
Studies on Ketogenic Diets and Insulin Resistance
Although, low calorie ketogenic diet in overweight helps to reduce weight, but evidence also shows it may impair insulin sensitivity. Effects of ketogenic diet are that they increase the risk of becoming insulin resistant. Improved insulin sensitivity is when glucose levels are optimal, but at reduced sugar levels, cells learn to ignore the insulin telling them to decrease glucose intake. Over time, it only furthers insulin resistance among cells. A few researches on this topic are:
- Research found that among people without any diagnosed diabetes, the risk of type 2 diabetes increases with a ketosis diet. The effect of KD when a person follows a ketogenic diet causes increased risk of becoming insulin resistant. As blood sugar isn’t controlled and sugar levels decrease abruptly, insulin sensitivity goes down
- Another study found feeding a ketogenic diet among people to increase risk only in the early days of the diet, rather than long-term risks. The study has noted that abruptly lowered glucose levels cause insulin sensitivity
- However, the study has also noted that the ketogenic diet induces more severe hepatic insulin resistance among individuals who are already at risk of developing diabetes
- Research limitations also show that findings on insulin resistance to an obesogenic fat diet are all very limited. There is not yet credible data to outright say that the ketogenic diet causes type 2 diabetes.
- Some studies even show improved insulin sensitivity, especially among patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Therefore, insulin-sensitizing effects are well-known from ketosis
- But others indicate impaired glucose metabolism and insulin resistance, especially long-term dietary restrictions following a ketogenic diet can impede diabetes management.
Differences between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
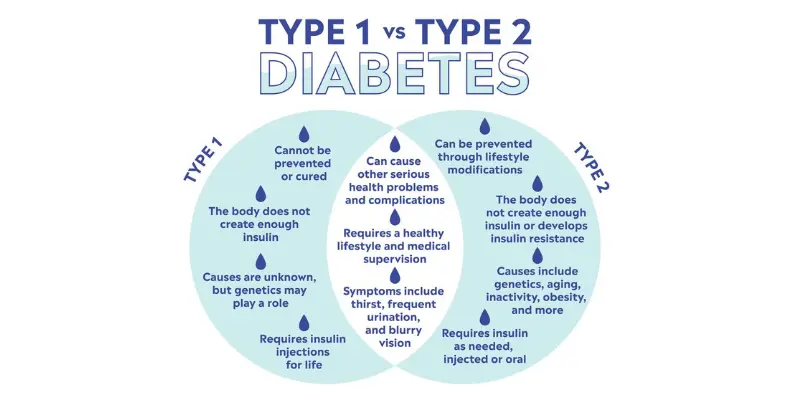
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are related to unequal levels of glucose and insulin in the blood, which affects the normal mechanisms of the body. Patients with diabetes also identify similar symptoms of thirst, blurred vision, headache, poor wound healing etc. However, there lies a major difference between the two, which is the reason for varying glucose and insulin levels.
T1D is autoimmune
Diabetes caused in type 1 is actually an autoimmune disorder, as the body’s immune system attacks insulin-making cells, considering them to be foreign. Research still does not know why our immune cells attacks the insulin making islet cells, but it results in pancreas not making any insulin.
People who are at risk of developing type 1 diabetes mellitus usually do so because of:
- Genetic causes
- Viral infections
- Certain foods and chemicals
T2D is linked to insulin resistance
Diabetes caused by type 2 is due to insulin resistance, as bodily cells stop responding to insulin, even though the pancreas is making insulin. The pancreas also makes less insulin in type 2 diabetes and it is linked to having too much body fat, which then results in cells not responding to the insulin.
People who are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus usually do so because of:
- Lifestyle
- Eating habits
- Obesity
- People aged over 45
Impacts of Ketogenic Diet Differs between T1D and T2D
Due to different causes for type 1 and type 2 diabetes, dietary changes like ketogenic state will also impact patients with diabetes differently.
- On type 1 diabetes, ketogenic diet causes a reduction in blood sugar, which can be useful in overcoming insulin resistance
- For type 2 diabetes, ketogenic diet abruptly decline blood sugar which can be a risk factor. However, with well-managed keto diet in which blood sugar is monitored and hyperglycemia is avoided, keto can actually promote a healthy blood sugar level and weight loss.
In both cases of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, it is worth noting that a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet causes an abrupt decline in blood glucose levels. In patients with diabetes, who are on diabetes medication to decrease blood sugar, this can considerably lower glucose levels and put the patient at risk. As opposed to a high-carbohydrate diet, ketosis completely cuts all external sources of glucose. For this diet group, however, this does not mean that they should completely avoid keto, instead it means that they should monitor their glucose levels keenly. Drink sugary drinks or eat sweets with the diet, to maintain blood sugar level
The effect of the ketogenic diet leads to insulin resistance, with fasting insulin being high as well as glucose levels being high. Diets in the management for KD diet, therefore recommends avoiding this diet for a long-term basis.
A Balanced Approach for Managing Diabetes
A well-formulated ketogenic diet avoids the risk of type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance and other effects of a ketogenic diet. Therefore, a balanced approach to ketosis is:
Blood Sugar
Ketogenic diets can help control blood sugars but monitor for side effects. Diet in patients with type 1 or 2, they must always monitor and check glucose levels before every meal. This will help in type 2 diabetes management, if you are a patient or impact of a ketogenic diet is known and reported. You will then be able to tell if certain foods lower blood sugar more or make you feel not happy
Low Carb
Although you are on a low-carb diet for ketosis, the assessment of insulin resistance and monitoring for low insulin will help you identify if this diet is negatively impacting you. With low carbs, you can even suppress any inflammation and insulin resistance. Following a ketogenic diet in patients or adults with type 1 diabetes, low carb, and low sugar will actually help to manage the condition
Whole Foods
Diet vs normal foods can have a detrimental effect on health, even if you are not following a low-carbohydrate diet in overweight adults. Focus on whole foods that meet the nutritional requirements of the body, without causing any harm. A few examples are:
- Avocado
- Eggs
- Protein (chicken or beef)
Exercise is Important
The etiology of type 2 diabetes, mechanisms of insulin resistance, response to insulin, and development to type 2 diabetes or type 2 diabetes are all related to lifestyle, to a certain extent. If you are not moving, your body and your weight keep increasing, then it is inevitable that your bodily functions will be affected. So, do exercise, follow a routine, and do it consistently.
Sleep for Optimal Insulin Sensitivity
In factors related to insulin resistance, not getting enough sleep can also impact glucose and insulin levels negatively. Research have shown that optimal of 8 hours of sleep in mice independent of weight loss, also improves metabolic mechanisms and insulin resistance. To set a control for type 2 diabetes or type 1 diabetes, sleep is essential.
Lifestyle Tips to Reduce Insulin Resistance
- Weight Loss for Overweight Individuals
A Keto diet simply for weight loss without any diagnosed disorders is great. Make sure that diet is a low-carb one and within 3 months, you can lose weight substantially
- Regular Physical Activity
In the keto diet, make sure you are also exercising. Whether the keto diet is causing weight loss or not, make sure to have some form of physical exercise every day
- Stress Management
Dietary restrictions can make one highly stressed, and with keto you have to do extensive planning and cannot eat the same food as others, so stress is a normal response. However, make sure you have plans for stress management. It can be hanging out with friends, planning meals that appeal to you, and monitoring bodily stats
- Adequate Sleep
Your rest is important. In adults with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, glucose, and insulin plasma levels are actually managed while you sleep, so make sure you are getting enough sleep
- Supplements Like Magnesium, Chromium, Berberine
A ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic diet can cut down on nutritional value from carbs. So, eat supplements to make up for the lost nutrition.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, ketosis will affects blood glucose levels, but in a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control, you have to make sure to monitor stats. Along with monitoring, you can also plan meals to manage blood glucose, insulin and other nutritional requirements. The key takeaways of this article are:
- Patients of type 1 diabetes can manage insulin and glucose levels, while patients of type 2 diabetes can manage insulin resistance by lowered blood glucose
- Studies on ketogenic diets show positive effects on insulin resistance, but an abrupt decline in sugar levels can also result in lowered insulin sensitivity from body cells, especially in the initial days
- Sleep, exercise, and monitoring are the best ways to follow ketosis in patients of diabetes.
FAQ’s:
Q. Is the Ketogenic Diet Good for Insulin Resistance?
Yes, ketogenic diet lowers blood glucose and can help overcome insulin resistance in cells
Q. What Foods to Cut Out For Insulin Resistance?
Processed foods that have high sugar content must be cut to avoid insulin resistance
Q. What Happens to Insulin Levels in Ketosis?
As blood glucose drops, insulin levels also decrease under ketosis
Q. What Carbs are Ok for Insulin Resistance?
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Grains
- Beans
Q. What Foods Spike Insulin Resistance?
Highly processed and sugared foods
Q. What Foods Decrease Insulin Resistance?
- Complex carbs
- Lean protein
- Fruits and veggies
- Dairy foods
Q. Does a Ketogenic Diet Reduce Insulin Resistance Long-Term?
Research is limited on this topic, as positive effects on insulin resistance from ketogenic diet have only been studied in the short term. In the short term we know that insulin resistance can be improved, but for the long term, research is needed.


